- TYPO Overview: Pages, Storage, Filelist, Blog, page view, list view
- Adding new pages
- Typical page content
- Grid elements
- Slideshows
Downloads
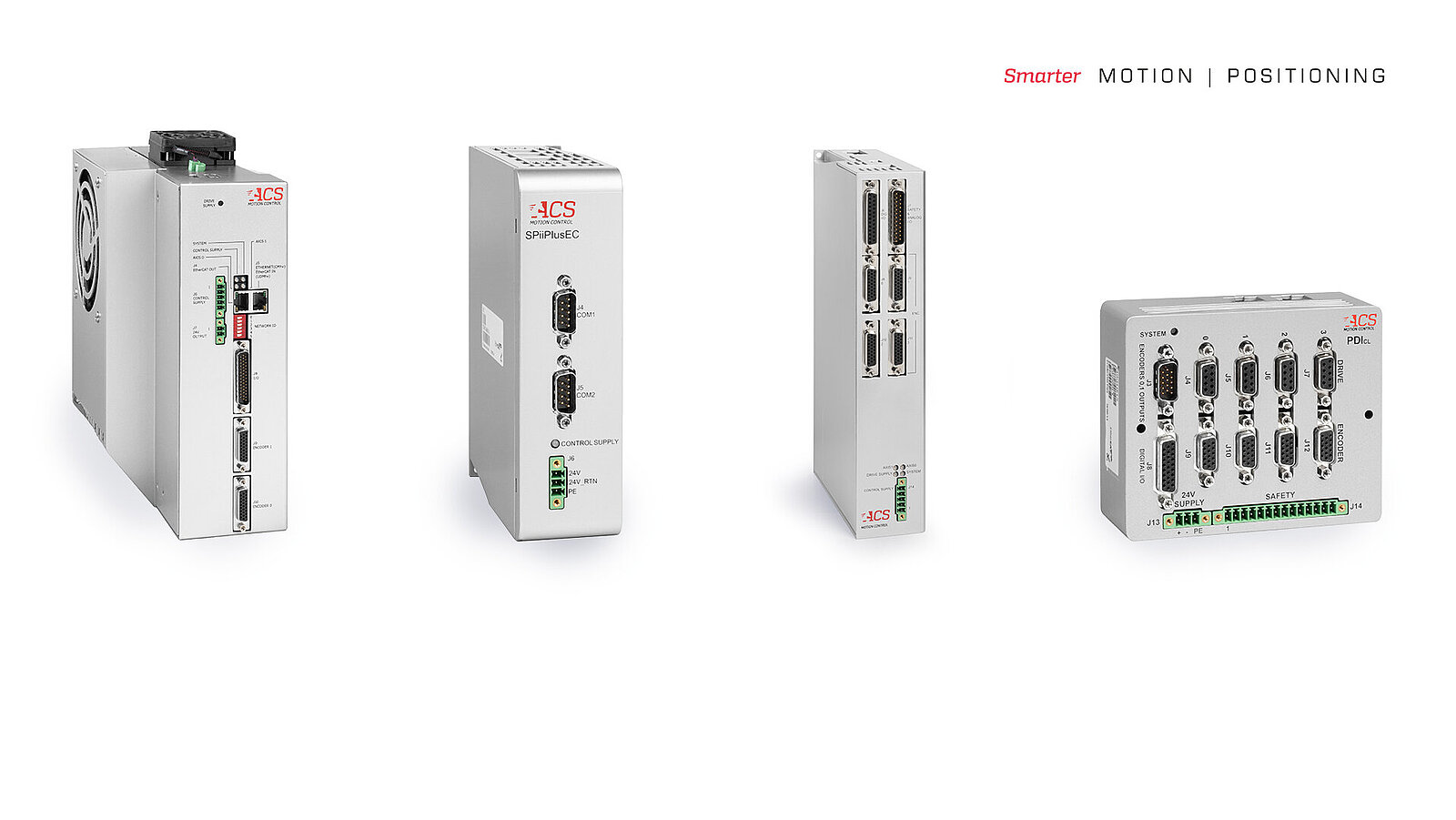
How to Optimize the Performance of Motion Platforms with ACS
Unique ACS Motion control Features Enhance Possibilities in Industrial Automation
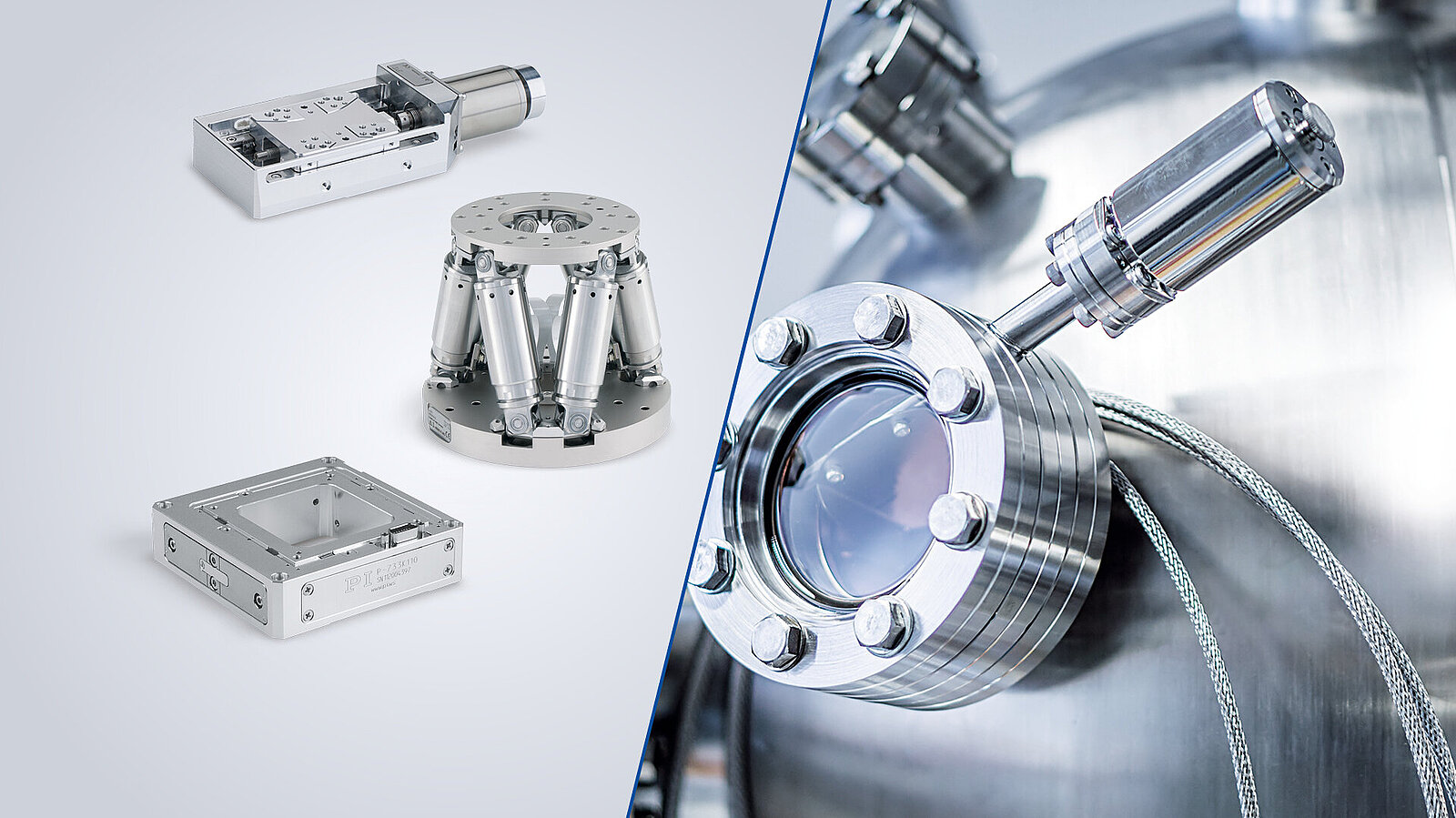
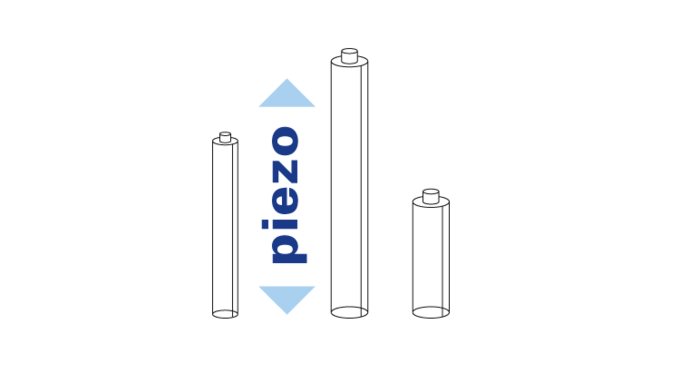
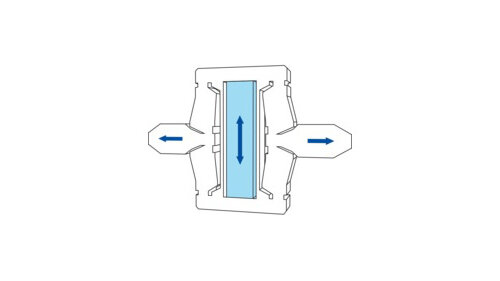
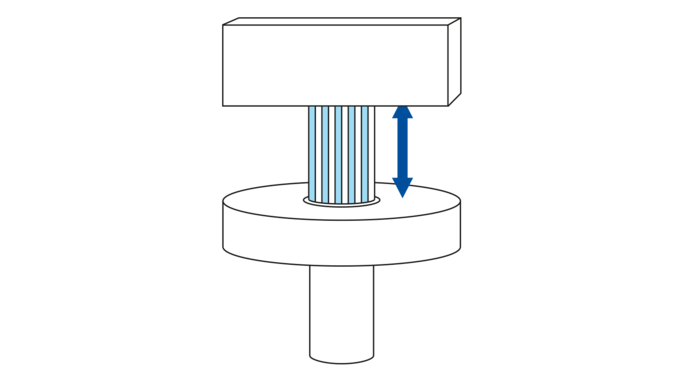
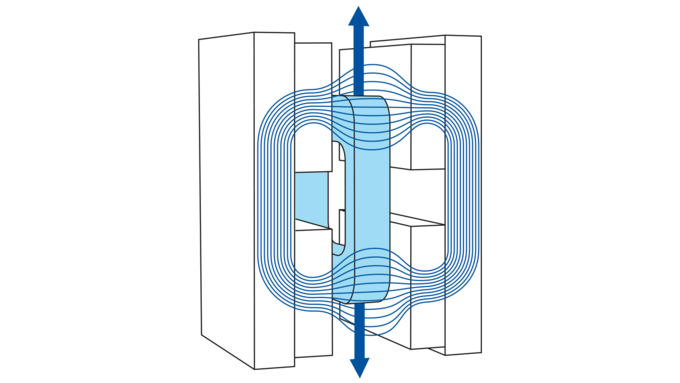
In total reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM), the laser beam hits the glass plate of a microscope slide, a microtiter plate or Petri dish at a flat angle in order to stimulate the fluorescence.
Nevertheless, the electromagnetic field of the laser beam does penetrate the sample volume on the other side of the glass plate and forms an evanescent field with a penetration depth between 100 to 200 nm. As a result of the reduction of the stimulated area in the Z direction, a better Z resolution is achieved than the standard wide field - or confocal fluorescence microscopy. Here, the Z resolution is typically 500 nm. That is the reason why TIRFM is more frequently used in fluorescence microscopy as a comparatively simple and inexpensive super resolution method.
In total reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM), the laser beam hits the glass plate of a microscope slide, a microtiter plate or Petri dish at a flat angle in order to stimulate the fluorescence.
Nevertheless, the electromagnetic field of the laser beam does penetrate the sample volume on the other side of the glass plate and forms an evanescent field with a penetration depth between 100 to 200 nm. As a result of the reduction of the stimulated area in the Z direction, a better Z resolution is achieved than the standard wide field - or confocal fluorescence microscopy. Here, the Z resolution is typically 500 nm. That is the reason why TIRFM is more frequently used in fluorescence microscopy as a comparatively simple and inexpensive super resolution method.